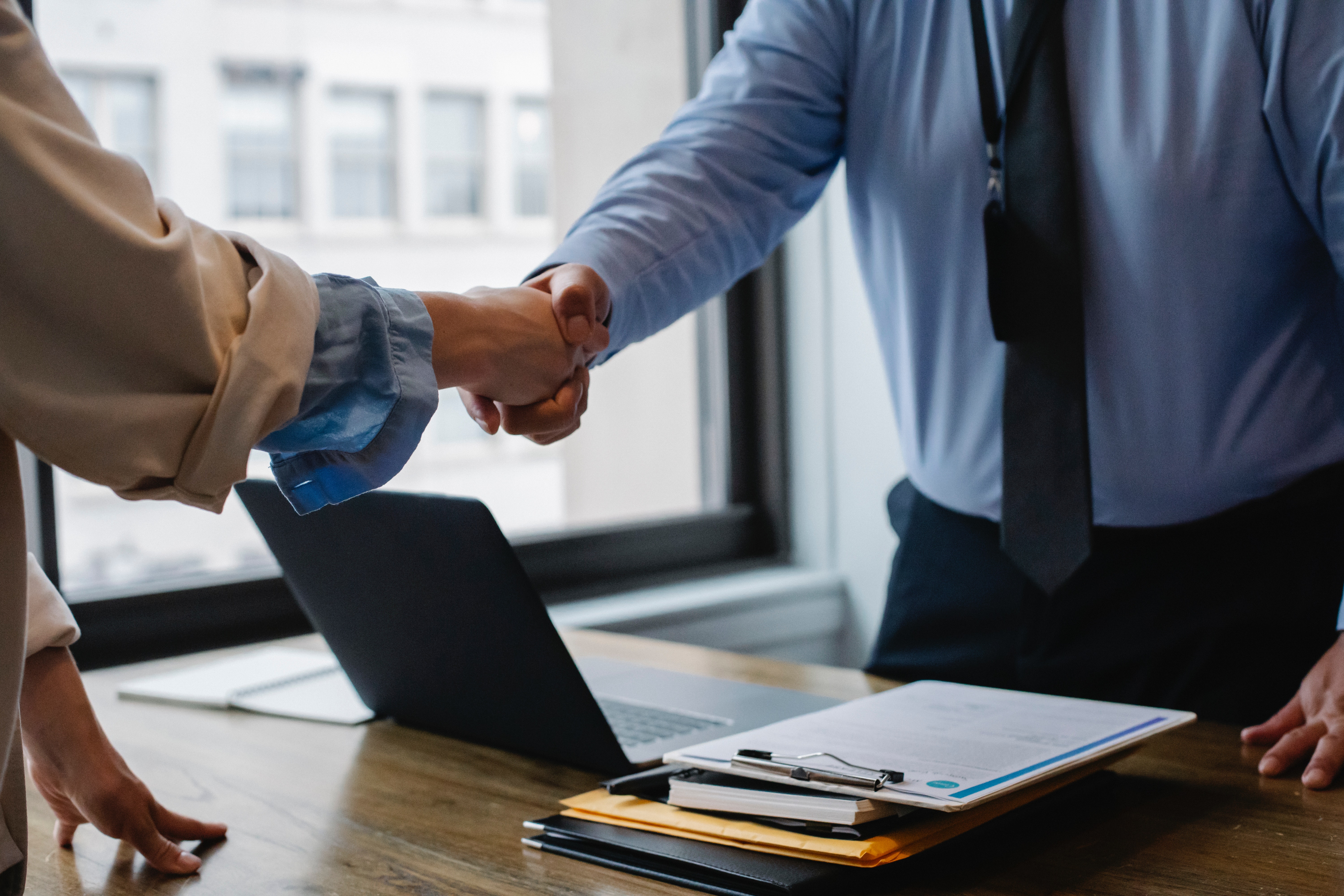
Do you want to set up offshore company for your business? Before that, you must understand what an offshore company is and the advantages and disadvantages to incorporate the same. An offshore company is one that is set up in a jurisdiction other than the home country of its owners. In this article, we highlight the benefits and drawbacks of setting up an offshore company.
What are the benefits of setting up an offshore company:
- Privacy and Security:
Setting up an offshore company would imply that the businesses receive additional privacy and security, owing to the strict government policies of the jurisdiction of your choosing. This will subsequently lead to a greater level of confidentiality and asset protection provided to businesses.
In several jurisdictions, businesses are not required to disclose the personal information of the business’s shareholders, directors, and unique beneficial owners. This protects the identities of the business’s stakeholders.
Moreover, in some jurisdictions, the investments made by the business and the asset of the business is not disclosed to any external parties or the public, thus securing the business even further.
Besides the above, setting up businesses in different jurisdictions allows for a diversification of risk which will lead to a decrease in the vulnerability of the business.
- Tax benefits and incentives:
The governing bodies of different jurisdictions have different policies set in place. This leads to different corporate tax rates levied on businesses. Furthermore, the government provides various tax incentives and exemptions to attract foreign direct investment. Setting up an offshore business in a suitable jurisdiction can allow for businesses to take advantage of the low tax regime followed by the government. The optimization of the tax burden that businesses must pay will allow them to grow and scale further.
Besides, if the government of your chosen jurisdiction has formed tax treaties with that of other countries, businesses might be safe from being subjected to double taxation.
- Stable political and economic environment:
If there were high levels of instability in the political and economic environment of your home country, it would be beneficial for your business to shift offshore to a more stable environment. This is because, in an unstable environment, there would be a reduction in investments made by individuals and businesses and would
By shifting your business to a more stable environment your business would suffer from a lower risk as opposed to that in the home country.
- Compliance requirements:
Businesses need to meet certain compliance requirements prior to and after the incorporation of the business which differs from country to country. In certain jurisdictions, businesses need to meet fewer requirements in terms of the number of directors and shareholders, the nationality requirement, the need for local offices, and more.
Moreover, businesses may face fewer accounting and tax filing obligations which makes it more convenient for the businesses to operate in the chosen jurisdiction.
- Infrastructure and labour force:
In certain jurisdictions, the government invests high amounts of funds in the development of infrastructure. This is done to attract foreign investment to the region. Thus, businesses set up in those jurisdictions will be able to take advantage of the well-developed infrastructure available.
Besides this, the labour force available in some jurisdictions may be inexpensive and vast in number. Businesses can also take advantage of the inexpensive labour available in the country, thus, reducing the overhead costs.
- Banking facilities available:
It is imperative that you also check the banking facilities available in the country of your choice. This is because you will require an offshore bank for your offshore business. Selecting a bank that is relatively inexpensive and easy to open is a factor that you must consider.
Besides this, you must also note the services that the bank provides for your business including internet banking, currency exchange services, multi-currency facilities, the opportunity to invest in international markets, and more. These services allow offshore businesses to not only conveniently conduct their business but also reduce any risk of currency fluctuation and investing in one portfolio.
What are the drawbacks of setting up an offshore company:
- Expensive incorporation process:
The cost of setting up your business offshore depends on the choice of your jurisdictions. The government of each country decides on the incorporation and legal fees that must be paid during the business registration process.
Moreover, some countries may require businesses to have a minimum paid-up share capital amount required during the incorporation process. This leads to a higher amount of money required by businesses to address these costs.
Therefore, it is imperative for you to understand the costs of each of the jurisdictions and decide on a suitable one for your business. For example: it is costlier to set up your business in the Cayman Islands than it is in Hong Kong or Singapore.
- Difficult to choose a suitable jurisdiction:
Deciding on a jurisdiction that will be suitable for your offshore business is difficult and requires a lot of research. You have to consider multiple factors when deciding on a jurisdiction for your business including location, business-friendly government policies, political and economic environment of the country, costs, banking facilities, infrastructures and labour force available, and more.
Moreover, you will need to compare different jurisdictions to decide on a suitable one for your business. Therefore, deciding on a suitable jurisdiction will be a time-consuming process.
- Negative perception:
Businesses set up in certain jurisdictions such as traditional tax havens including the Cayman Islands, British Virgin Islands, and more are subjected to negative perception. This may be disadvantageous for the business’s reputation as the public may believe the business is attempting to do so to evade tax even if that reasoning is invalid and not true.
- Proving ownership:
Since businesses are provided with high levels of privacy that do not require them to disclose the personal information of the various stakeholders of the business, it may be difficult to prove the ownership of the offshore business. This is because there will not be a publicly maintained record proving the same.











Разберём XCARDS и стоит ли ей доверять?
Пару дней назад наткнулся на интересный сервис XCARDS, что позволяет выпускать онлайн банковские карты чтобы контролировать расходы.
Ключевые преимущества:
Создание карты занимает несколько
минут.
Сервис позволяет выпустить любое число карт — без
ограничений.
Есть поддержка круглосуточно и даже через
менеджера в чате.
Все операции отображаются
моментально — лимиты, уведомления, отчёты, статистика.
Потенциальные риски:
Локация компании: офшорная зона
— перед использованием стоит уточнить,
что сервис можно использовать без нарушений.
Финансовые условия: карты заявлены
как “бесплатные”, но дополнительные
сборы, поэтому советую внимательно изучить условия.
Отзывы пользователей: по информации в сети реагируют по-разному — от минуты до часа.
Безопасность: сайт использует шифрование, но
всё равно советую активировать 2FA.
Заключение:
Если всё заявленное соответствует действительности — XCARDS выглядит как
полезным сервисом для бизнеса.
Платформа сочетает удобный интерфейс, разнообразие BIN-ов и простое управление.
Как вы думаете?
Есть ли у вас опыт с виртуальными картами?
Расскажите, как у вас работает Виртуальные карты для цифрового маркетинга
Забронируйте комфортное жильё уже сегодня
и наслаждайтесь комфортным отдыхом.
Где снять квартиры
@airbn@b77
Действительно….такой выгодный веб-страница.
Посетите также мою страничку Где снять квартиры https://tiktur.ru/
Советы по аренде жилья на сутки
1. Определите бюджет и даты поездки.
2. Поставьте приоритеты — комфорт, стоимость или расположение.
3. Читайте отзывы и смотрите рейтинг.
4. Бронируйте заранее.
Квартиры на сутки
@airbn@b77 https://sutochny.ru/poleznyye-sovety/
Very shortly this site will be famous amid all blogging and site-building people, due to it’s fastidious content https://meds24.sbs/
Привет, знаешь, как легко платить криптой через
QR?
Криптовалюты сейчас штурмуют мир, и это не просто слова!
Забудь про долгие переводы или возню с
кошельками — QR-код решает всё!
И знаешь, это не так сложно, как кажется!
QR-код на чеке? Плати криптой!
Серьёзно, первый раз оплатил такси криптой через QR, и это было легко и быстро.
Просто взял телефон, навёл камеру на QR-код, и всё, сделка в кармане!
Попробуй, и поймёшь, почему все об этом говорят!
Как платить криптой по QR?
Секрет прост: нужен приложение для крипты.
Выбери кошелёк типа Trust Wallet — главное, чтобы
QR-коды умел считывать. На кассе или в интернет-магазине тебе дают QR-код, ты его просто фоткаешь, подтверждаешь сумму,
и всё — оплата ушла! QR-оплата криптой: удобно для клиента
Самое крутое — это скорость. И главное — безопасно: QR-коды защищают транзакцию.
Попробовал оплатить подписку — и ни одной проблемы, всё как надо!
Где можно платить криптой по QR?
Платить криптой через QR можно уже в куче
мест. Видел, как в сервисах всё чаще берут крипту по QR?
Ищи логотипы криптовалют или спроси на кассе — продавцы обычно знают.
Оплата будущего
В интернете вообще сказка: многие магазины уже поддерживают QR-оплату
криптой. Заходишь на сайт, выбираешь «Оплатить криптовалютой», сканируешь QR-код, и оплата прошла!
Попробовал оплатить онлайн-курс через
QR — и это было как два пальца.
Почему это круто?
Платить криптой через QR
— это как жить в 21 веке. Ты не
зависишь от банков, комиссий за переводы и прочей головной боли.
А ещё это не светит твои финансы, что
всегда плюс.
Честно, платить криптой через QR — это прям кайф!
Сканируешь QR, подтверждаешь, и бац — ты уже на волне технологий!
Просто попробуй — это реально круто!
Больше клиентов: предложите оплату криптой по QR
Ну что, в деле?
Честно, оплата криптой по QR-коду — это реальная тема, и оно уже здесь!
Сделай одну оплату через QR, и, спорим, ты не захочешь иначе?
Просто открой приложение, найди место,
где принимают крипту, и вперёд!
Есть опыт оплаты криптой через QR?
расскажите, как всё прошло!
Почему стоит платить криптой через QR-код https://tinyurl.com/antarctic-wallet
Поддерживать исключительную работу!!
Люблю это! Посетите также мою страничку Территория обратных ссылок https://linksbuilder.fun/
Эй, слышал про оплату криптой по QR-коду?
С криптой жизнь становится проще, согласен?
Забудь про долгие переводы или возню с кошельками — QR-код решает всё!
А главное — это реально удобно, сейчас объясню.
Крипта для ленивых: просто отсканируй
Я сам недавно втянулся эту тему,
и, честно, впечатления огонь!
Больше не нужно вбивать кучу данных.
Это реально затягивает, держу пари,
тебе зайдёт.
Что за магия с QR-кодом?
Чтобы оплатить что-то криптой по QR-коду, тебе нужен цифровой кошелёк с поддержкой QR.
Скачай, например, Trust Wallet, или любое приложение, где есть сканер QR-кодов.
На кассе или в интернет-магазине тебе дают QR-код, ты
его сканируешь, подтверждаешь сумму, и
всё — оплата ушла! Всё меняется: крипта и
QR на службе у кошелька
Самое крутое — это скорость. Плюс, это безопасно:
QR-код шифрует данные, так что твои USDT в надёжных руках.
Я как-то оплатил доставку
пиццы через QR, и всё прошло
гладко, как по маслу!
Куда с криптой и QR-кодом?
Платить криптой через QR можно уже в куче мест.
Например, в некоторых кафе в больших городах уже принимают ETH через QR-коды.
Просто ищи значок крипты на кассе или спроси у продавца — они обычно знают, как это работает.
Блокчейн — в один скан
В интернете вообще сказка: многие магазины уже поддерживают QR-оплату криптой.
Заходишь на сайт, выбираешь «Оплатить криптовалютой», сканируешь QR-код, и всё готово!
Попробовал оплатить онлайн-курс через QR —
и это было как два пальца.
Зачем тебе платить криптой
по QR?
Платить криптой через QR — это как быть на волне.
Забудь про банковские комиссии — крипта и QR решают всё!
А ещё это держит всё в секрете, что всегда плюс.
Честно, платить криптой через QR — это прям кайф!
Сканируешь QR, подтверждаешь, и бац — ты уже в деле!
Попробуй сам, и поймёшь, о чём я!
QR-платежи с криптой
Готов попробовать?
Честно, оплата криптой по QR-коду — это будущее, и оно уже здесь!
Попробуй один раз, и, держу пари, ты не захочешь возвращаться к старым
способам. Просто установи аппку, найди место, где принимают
крипту, и вперёд!
Кто-нибудь уже пробовал QR-оплату?
Делитесь, как оно?
Smart Crypto Scan — Умная крипта по QR https://tinyurl.com/4h7kcs2r
Друзья — кто уже тестил, что такое обратные ссылки?
Недавно поймал себя на мысли и понял —
бэки — это как кислород для сайта.
Тестил разные методы — от краудов
до гостевых постов, но результат нестабилен.
В итоге нашёл способ, который реально
работает.
Не буду спойлерить, но вот ссылка — вот тут обратные ссылки .
Ребята подробно расписали схему.
Результаты приятно удивили — особенно по конкурентным запросам.
Реально советую — инфа стоящая.
Кому нужно — ссылка выше https://kwork.ru/bulletin-boards/5649/otpravlyu-na-registratsiyu-v-1500-katalogov-saytov
Indexing and power checking Service for Google and Yandex.
fast indexing windows download
World Health Organization terminate benefit from this service?
This religious service is useful for site owners and SEO specialists WHO want to increment their visibility
in Google and Yandex,
amend their land site rankings, and step-up constitutional dealings.
SpeedyIndex helps promptly forefinger backlinks, newfangled pages, and web site
updates. fast indexing api https://t.me/SpeedyIndexBot?start=206352122
Indexing and indicator checking serve for Google and Yandex.
Backlink Workshop
World Health Organization canful do good from this avail?
This table service is utilitarian for site owners and SEO specialists who desire to increment their visibility in Google and
Yandex,
ameliorate their locate rankings, and gain organic fertilizer dealings.
SpeedyIndex helps quickly forefinger backlinks, raw pages, and site updates.
Backlink Workshop https://linksbuilder.fun/
Hello there I am so glad I found your blog page,
I really found you by mistake, while I was looking on Bing for something else,
Anyways I am here now and would just like to say cheers for
a fantastic post and a all round interesting blog (I
also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to browse it all at the moment but I have bookmarked it and also added your
RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read much more,
Please do keep up the awesome work. https://truepharm.org/
Большое спасибо очень полезно.
обязательно поделюсь сайтом с
моими приятелями. Посетите также
мою страничку Как выбрать гостевые дома посуточно https://www.findyourwings.co.za/2020/05/21/gratitude-gives-you-wings/
Эй, слышал про оплату криптой по QR-коду?
Криптовалюты сейчас взрывают мир, и это не просто слова!
Представь: ты в кафе, заказал вкусный
латте, а вместо карты или налички просто сканируешь QR-код и — бац!
— оплата ушла за секунду. А главное — это реально удобно, сейчас
объясню. Принимайте криптовалюту по QR-коду —
легко и быстро
Я сам недавно втянулся эту тему, и,
честно, просто вау! Больше не нужно вбивать кучу данных.
Попробуй, и поймёшь, почему все об этом говорят!
Как это работает?
Секрет прост: нужен телефон
с криптокошельком. Скачай,
например, MetaMask, или любое приложение, где есть сканер
QR-кодов. В магазине или онлайн тебе показывают QR-код, ты его открываешь в приложении, жмёшь «Оплатить», и
готово! QR Crypto Checkout — Расчёт криптой
через QR
Самое крутое — это скорость. И главное — безопасно: QR-коды шифруют данные.
Попробовал оплатить кофе — и ни
одной проблемы, всё как надо!
Куда с криптой и QR-кодом?
Платить криптой через QR можно уже
в самых разных точках. Например,
в некоторых магазинах в больших городах уже принимают USDT через QR-коды.
Ищи логотипы криптовалют или
спроси на кассе — всё просто, если уточнить.
Увеличьте продажи: криптовалютная оплата по QR
Онлайн это ещё проще: многие сервисы добавляют оплату криптой через
QR. На сайте жмёшь «Оплатить криптой», сканируешь QR,
и всё в порядке! Попробовал оплатить онлайн-курс через QR — и это было как два пальца.
Чем QR-оплата цепляет?
Оплата криптой по QR-коду — это не только удобно, но
и шаг в будущее. Забудь про лишние проверки — крипта и QR решают
всё! Плюс, это анонимно, если тебе важна
приватность.
Честно, платить криптой через QR
— это прям кайф! Когда ты
сканируешь код и видишь, как эфир улетают за покупку, чувствуешь себя человеком будущего.
Рискни, и тебе точно зайдёт! удобно
Ну что, в деле?
Честно, оплата криптой по QR-коду — это реальная
тема, и оно уже здесь! Сделай одну оплату через QR, и,
спорим, ты втянешься? Бери телефон, сканируй
QR — и делись впечатлениями!
Кто-нибудь уже заценил этот способ?
Делитесь, как оно?
Будь на шаг впереди: плати криптой через QR https://glencoenews.com/places/hollywood-heating-and-air/
Спасибо действительно полезно.
Буду поделюсь веб-сайтом с моими приятелями.
Посетите также мою страничку заказать дебетовую карту на дом дебетовая
карта года альфа банк дебетовая карта https://nurenergie.com/modules/babel/redirect.php?newlang=fr_fr&newurl=http://kugatsu.Flop.jp/9cgi/9kansoubbs2013/9nmaruchan.cgi%3F
Рассмотрим подробнее XCARDS — платформу, которая
меня заинтересовала.
Пару дней назад обнаружил на финансовый проект XCARDS, что позволяет выпускать
цифровые банковские карты чтобы оплачивать сервисы.
Что обещают:
Создание карты занимает считанные минуты.
Пользователь может оформить
неограниченное количество карт.
Есть поддержка в любое время суток включая персонального менеджера.
Есть контроль онлайн — лимиты,
уведомления, отчёты, статистика.
Возможные нюансы:
Регистрация: офшорная зона — желательно убедиться, что сервис
можно использовать без нарушений.
Комиссии: в некоторых случаях встречаются скрытые комиссии,
поэтому рекомендую просмотреть
договор.
Отзывы пользователей: по комментариям в Telegram вопросы решаются оперативно.
Надёжность системы: внедрены базовые меры безопасности, но всё равно советую активировать 2FA.
Заключение:
Если всё заявленное соответствует действительности — XCARDS выглядит как
удобным инструментом для фрилансеров.
Он объединяет удобный интерфейс, разнообразие BIN-ов и простое управление.
Как вы думаете?
Пробовали ли подобные сервисы?
Напишите в комментариях Виртуальные
карты для онлайн-платежей https://baoly.ru/antarctic_wallet